A shared SAN data server is a Linux based file server which can be accessed through Fibre channel interconnect.
You can use a SAN data server to do the following:
-
Export mount points through fibre channel to multiple MediaAgents.
-
Share a mount path without setting up network sharing configurations such as NFS, CIFS, UNC share.
Key Features
-
Multiple MediaAgents of different platforms can transfer data to the SAN data server simultaneously
-
Storage consolidation as you do not have to provision storage individually to each of the MediaAgents and any existing free space can be used by all the MediaAgents
-
The consolidated storage can be shared across all the MediaAgents and the data written by one MediaAgent is accessible to all the other MediaAgents.
The following MediaAgents are supported:
-
Windows
MediaAgents on windows clusters are not supported with Shared SAN Data Servers.
-
Linux
-
AIX
-
-
Global deduplication of the data
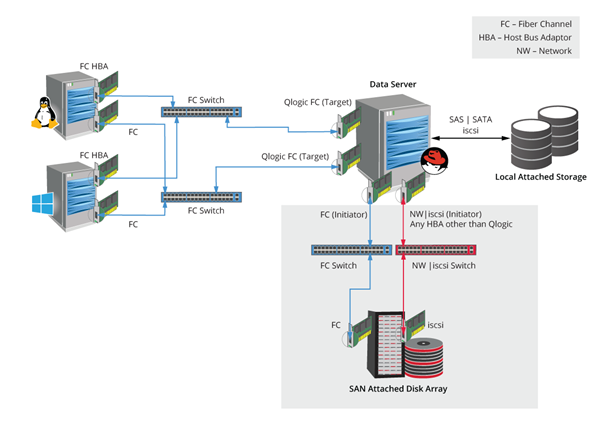
Configuration Modes
You can configure the shared SAN data server depending on the way in which the storage is provisioned to the data server and the transportation type through which the mount path is shared with all the MediaAgents.
The following three modes of storage are supported:
-
Direct attached storage mode
In the direct attached storage mode the MediaAgents can access the mount points that are created on the disks that are directly attached to the SAN data server through SCSI transport types, such as SAS and SATA.
-
SAN attached storage mode
In the SAN attached storage mode the mount points that are created on the disk array which are connected through fibre channel or iSCSI are accessed by the MediaAgents.
-
The mixed mode
In the mixed mode is a combination of the direct and SAN attached storage mode.
For more information on determining your configuration preference, see Determining the Configuration for the Shared SAN Data Server