Commvault provides virtual private network (VPN) services to enable controlled access to resources in your private network. For example, you can use a laptop at a home office to access your work office computer.
Commvault VPN services operate under the VPN router and VPN client model. The VPN client allows you to establish connections with a private resource, while the VPN router controls the VPN traffic between the VPN client and the private resource. A private resource is a computer, server, or any TCP/IP device in your private network.
For instructions about how to configure VPN services in your environment, see Setting Up VPN Services. Setup instructions are intended for the CommCell administrator.
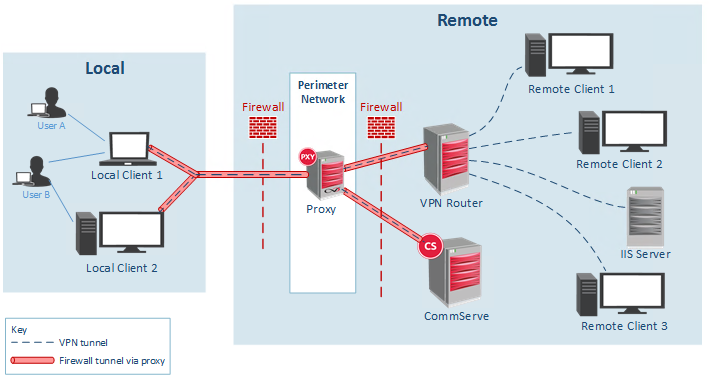
VPN Router
The VPN router is a client or client group that is located behind the firewall. The router receives connection requests through a firewall tunnel from VPN clients, then the router applies access control list (ACL) rules to allow or deny connections. If you need to provide access to distinct local area networks (LAN), you can configure multiple routers.
The VPN router controls access based on the following parameters:
-
User name or user group membership
-
Client name or client group membership
-
IP address or hostname of a service-providing computer
-
TCP port
For example, you can configure rules to allow or deny access for specific users or user groups. Access can be controlled through user and user group permissions that exist on the VPN client.
VPN Client
The VPN client is a desktop or laptop computer that runs the Commvault VPN Access software. The software enables the computer to establish VPN connections with a private resource through the VPN router.
Private resources do not need to have the Commvault software installed, but they must be reachable by the VPN router.