In the event of a disaster, recovery time can be minimized by having a stand-by site for disaster recovery. The following features support disaster recovery for virtual machines protected by the Virtual Server Agent (VSA) for VMware:
-
Full system recovery to a stand-by server
-
Live Mount for validation of virtual machine backups
-
Live Sync for automatic replication of virtual machines from backups to a disaster recovery site
Note
For the vCenter server, see Protecting and Recovering a vCenter Server.
Preparing for a Full System Recovery
While virtual machines can be restored at any time, restoring multiple virtual machines in a single operation can take a significant amount of time. Disaster recovery scenarios may require large numbers of virtual machines to be readily available at the moment they are needed.
To achieve this, a disaster recovery plan includes creating a stand-by server at a disaster recovery (DR) site to which virtual machines are restored on a routine basis. In the event of a disaster, the stand-by server is readily available with the virtual machines. After the initial creation of virtual machines on the stand-by server, incremental backups from the production site update only new or changed blocks (dash copy) for virtual machines on the stand-by server.
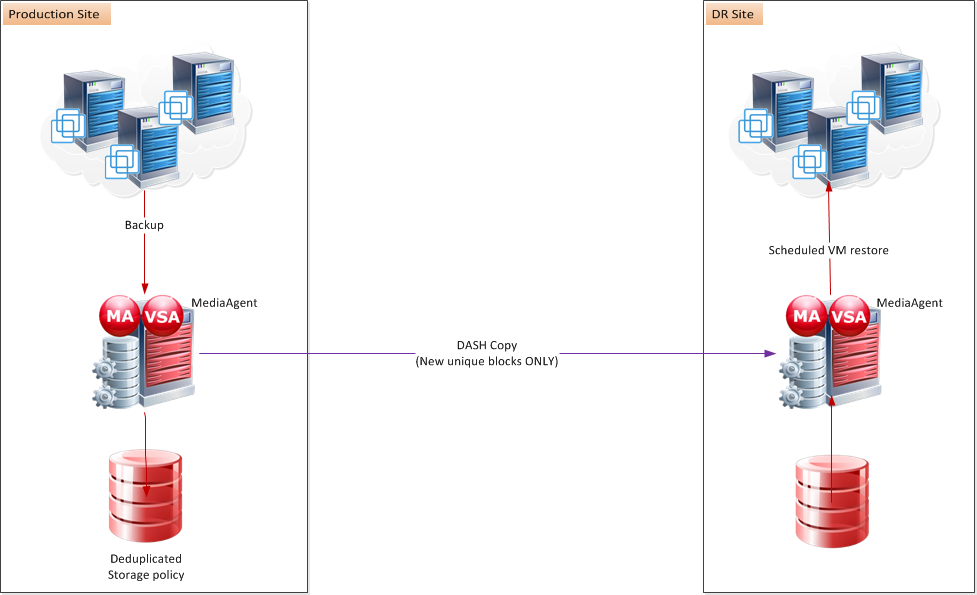
A stand-by server consists of the following:
-
The VMware application
-
Sufficient memory and disk space to hold all the virtual machines you may need to recover in a disaster scenario.
-
Both the primary and disaster recovery sites must include a MediaAgent and VSA proxy:
-
Add the VSA proxy for the primary site to the VMware instance and the subclient that is used for backups.
-
Specify an appropriate storage policy for the subclient. The primary copy for the storage policy specifies the primary site backup location, and the secondary copy specifies a backup copy location that is used for disaster recovery.
-
Recovering Full Virtual Machines
To recover full virtual machines in the event of a disaster, see Recovering Virtual Machines for VMware.
Reverting to the Production Server
After failing over to a disaster recovery site, you can restore services at the original production site or identify a new production site. To fail back to the production site, you can use one of the following approaches:
-
If you failed over to a standby server, you can reverse the failover operation by performing the following steps:
-
Back up the virtual machines on the standby server to capture any changes that were made after the failover.
-
Perform full VM restores to the production server. If you are restoring to the original production server, use the unconditional overwrite option for the restores.
-
-
If you set up the disaster recovery site using the Live Sync feature, perform a failback operation.