Overview
Storage Area Networks (SAN) present additional configuration issues, that are discussed in the following sections.
Stop and disable Removable Storage Management (RSM) service on all Windows 2000 on a SAN, which can detect the shared tape drives that are configured. These include other MediaAgents and even other machines which do not have any components installed. This is a very stringent requirement as data corruption occurs if both RSM and MediaAgent running on any machine in the SAN access the same drive at the same time.
We strongly recommend that in a SAN based environment, hardware zoning of tape drives be implemented so that only the designated MediaAgents can detect and control the devices. This will minimize unnecessary monitoring and access to the devices from non-designated machines.
The Basic SAN Setup
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a Fibre Channel network that is dedicated to carrying backup data. SAN enhances backup and restore performance and eases congestion on an enterprise's Local Area Network (LAN), freeing it for normal business activities and communication. You can configure your SAN environment to take advantage of the Dynamic Drive Sharing (DDS) feature to share drives among multiple MediaAgents in a CommCell® group within a SAN environment.
Basic SAN components include:
Host Bus Adapter (HBA)
Each computer that is attached to a fibre network needs a special adapter, an HBA, that can send and receive signals across Fibre Channel cables.
Bridge, Router or Gateway
These pieces of equipment translate fibre signals to signals that can be understood by SCSI devices (fibre-to-SCSI communications) and vice versa. A gateway can also communicate between a Fibre Channel network and native fibre devices (fibre-to-fibre communications). Bridges, routers, and gateways are used to connect servers and storage devices to the SAN.
Hub
In a Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL) (see below), the hub is the fault-tolerant center of the network to which servers and storage devices are connected.
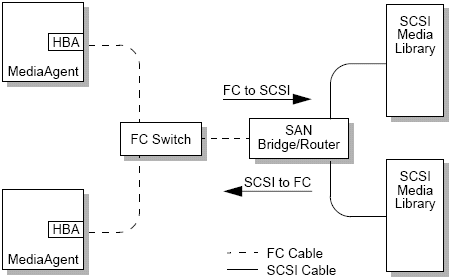
Switch
In the more complex network environment of switched fibre (see below), the switch is the center of the fabric, or infrastructure, of the network. Servers and storage devices are connected to the switch, which is more intelligent and has more bandwidth than a hub.
There are two basic SAN configurations:
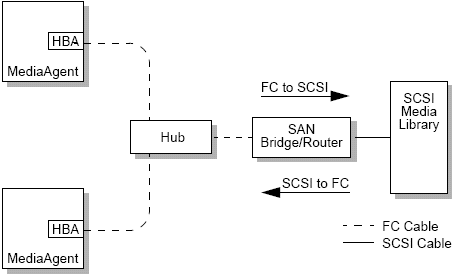
Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL)
This configuration is logically equivalent to a logical ring of fibre to which all of the devices are connected. FC-AL is implemented by connecting devices to a hub. Bandwidth and storage resources on the network are pooled and shared by all devices
Switched Fibre
In a switched configuration, virtual loops are established between hosts and backup devices. Each host may have exclusive use of its virtually attached storage devices.