There are cases in which direct connectivity setups do not work. Consider the case of the CommServe and MediaAgent being located inside a company’s internal network, with the entire network being exposed to the outside world through a single IP address. Typically, this IP address belongs to a firewall or gateway that works as a network address translation (NAT) device for connections from the internal network to the outside. The Commvault network supports NAT operations.
In scenarios like this, you can establish port forwarding at the gateway to forward connections received by specific gateway ports to clients on the internal network. You can then configure the clients to open a direct connection to the port-forwarder’s IP address on a specific port to reach a particular internal server. This creates a custom route from the client towards the internal servers.
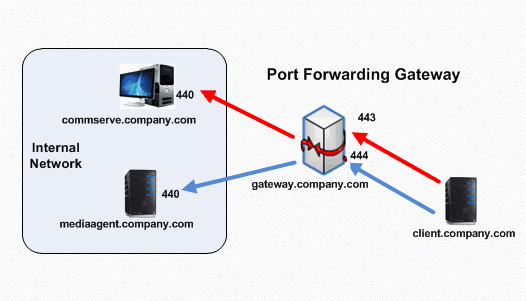
A port-forwarding gateway sends incoming connections to specific machines on the internal network based on the incoming connection’s destination port number.
The following diagram illustrates a client connecting to the CommServe and MediaAgent computers through a port-forwarding gateway setup.
Note
Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) uses port number 443 by default. If you are running IIS on a computer, you will not be able to use port 443 as a network route configuration on that computer. By default, the Commvault software uses port 8403 for network communication.
Process Flow
-
Set up the CommServe computer to listen for connections from the gateway. For more information, see Setting Up Connections from the Port-Forwarding Gateway to the CommServe Computer.
-
Install the Commvault software on one or more clients. During client installation, configure the client to connect to the CommServe computer through a port-forwarding gateway. For network settings instructions during the installation, see Setting Up Connectivity to the CommServe Computer Through a Port-Forwarding Gateway.
-
Perform network configurations on the CommServe computer to recognize the client connections through the port-forwarding gateway. For more information, see Configuring the CommServe Computer.
-
Perform network configurations on the MediaAgents to recognize the client connections through the port-forwarding gateway. For more information, see Configuring the MediaAgents.
-
Perform network configurations on the clients to establish the appropriate connections with the CommServe and MediaAgent computers. For more information, see Configuring the Clients.