System State must be added in Active Directory servers to perform Active Directory restores.
It is recommended that you perform a restore operation immediately after your first full backup to understand the process. Keep in mind that any object or attribute is restored to the same location from where it is backed up. The following section explains how to restore the Common Name (CN) Guests.
-
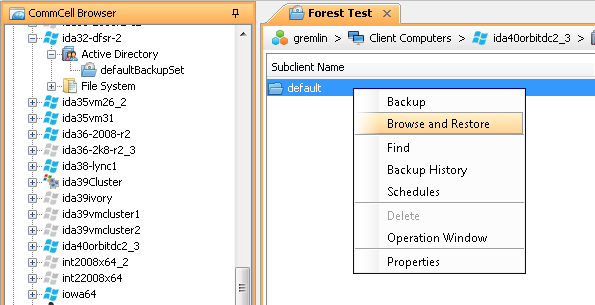
From the CommCell Browser, navigate to Client Computers| <Client>| Active Directory | defaultBackupSet
Right-click the default subclient and then click Browse and Restore.
-
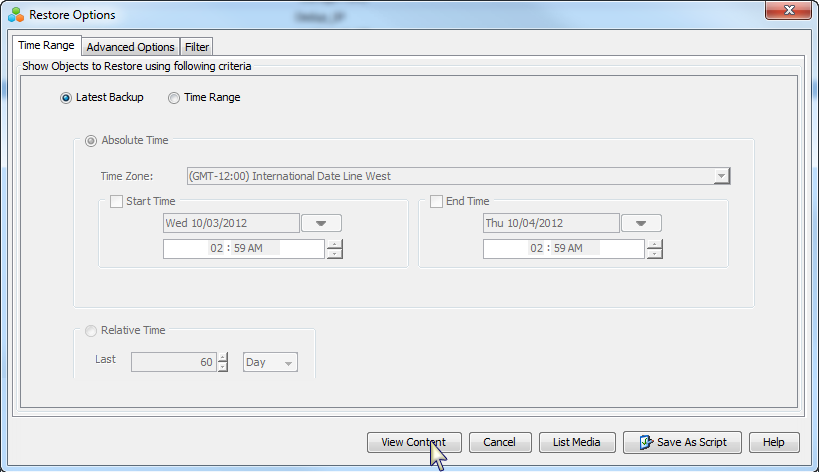
Click View Content.
-
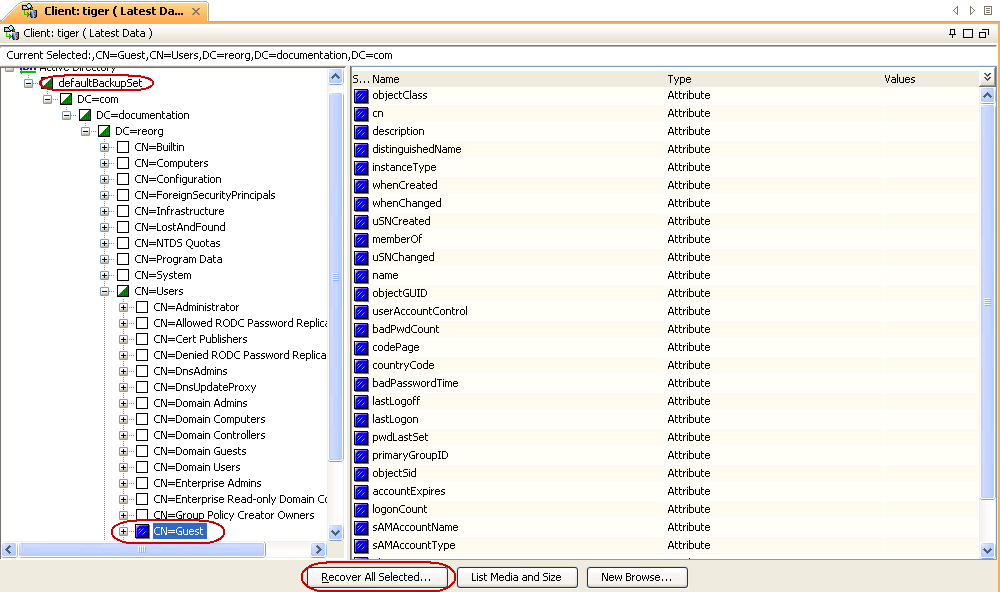
Expand the defaultBackupSet and navigate to the required Domain Component.
Select the CN Guest.
All the attributes of the object are selected by default.
For the first restore job, select any object with smaller data size.
Click Recover All Selected.
-
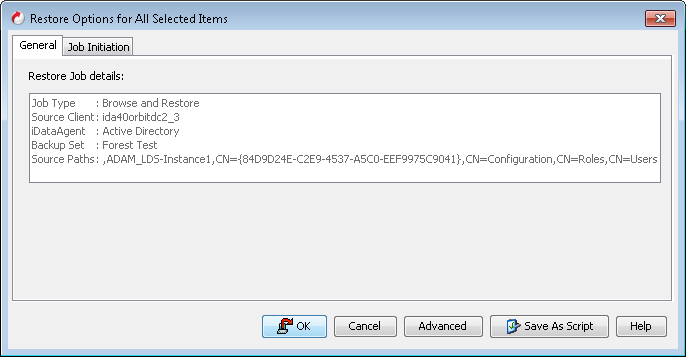
By default, the object and its attributes are restored to the same location from where they are backed up.
If you have modified the object or attribute after the first backup, you may lose the changes.
-
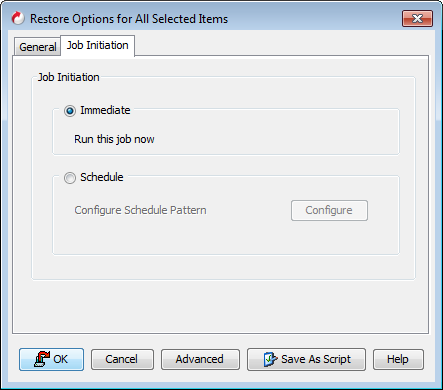
Click the Job Initiation tab.
-
Select Immediate to run the job immediately.
-
Click OK.
-
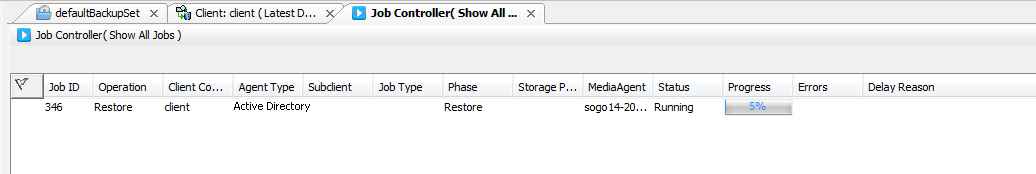
You can monitor the progress of the restore job in the Job Controller window of the CommCell Console.
-
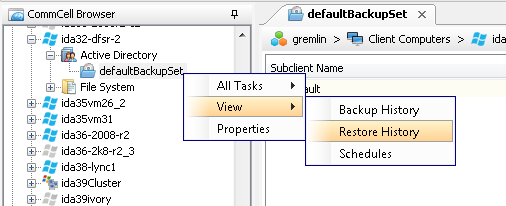
Once the restore job is complete, right-click the defaultBackupSet , point to View, and then click Restore History.
-
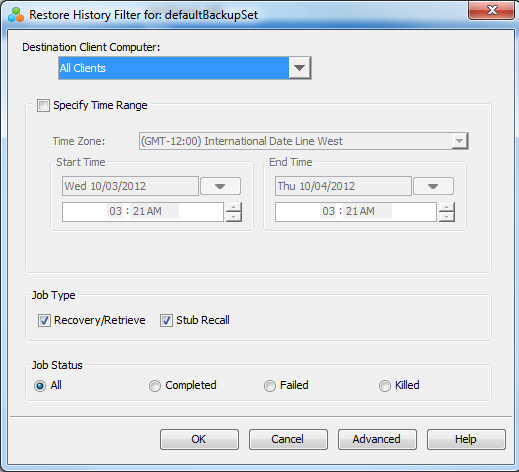
Click OK.
-
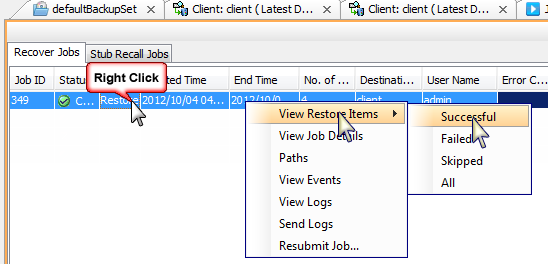
You can right-click the job and view the following details:
-
View Restore Items
-
You can view them as Successful, Failed, Skipped or All.
-
View Job Details
-
View Events of the restore job
-
View Log files of the restore job
-
-
Once the restore jobs complete successfully, verify that the restored objects/attributes are available in the domain controller.
What Is Restored
Attributes on each supported Windows object
Computer
Contact
Group
InetOrgPerson
MSMQ Queue Alias
Organizational Unit
Printer
User
Shared Folder
Configuration
Schema
ForestDNSZones
DomainDNSZones
What Does Not Get Restored In-Place
Due to a Microsoft limitation the following attributes are backed up but cannot be restored in-place. If the Update Privilege value is set by the system, then the attributes cannot be restored in-place. For example, the Bad-Password-Time attribute is not restored in-place as the Update Privilege value is set by the system. For more information on the available attributes and restoring a deleted active directory object, see All Attributes and Restore a Deleted Active Directory Object.
ObjectGUID
ObjectSid
PrimaryGroupID
BadPasswordTime
LastLogoff
LastLogon
MemberOf (Although this is a non-modifiable attribute and you cannot restore it directly, when a user or group object is restored the members will be placed back in the group)
PwdLastSet (only if adldaptool.exe was executed before the backup)
USNChanged
USNCreated
WhenChanged
WhenCreated
DistinguishedName
UserAccountControl
Delete Objects
rootDSE object
SID-History (only if adldaptool.exe was executed before the backup)
GivenName (Active Directory Agent uses the Distinguished Name (DN) to locate the object in live AD during a restore operation. GivenName is a part of user's DN. If a user name is changed or renamed, you cannot locate the AD object for restores. In that case, the restore operation.)
Restoring User Accounts and Passwords
When you back up an user account, the user's password is not restored along with the user account. The user's password hash stored in the unicodePwd attribute is not read due to security reasons. When a user is deleted, the user object is moved to the AD tombstone container. The deleted user object in the tombstone does not preserve all the original attributes. During a restore operation, the user object is "undeleted" from the tombstone, and then the attributes that are not preserved are deleted. The user account is restored with the last password.
If unicodePwd attribute is preserved, you can restore the last stored password before the user is deleted. Point-in-time restores are not supported as the password is not stored in Commvault backup operations. For more information, see Microsoft article unicodePwd.