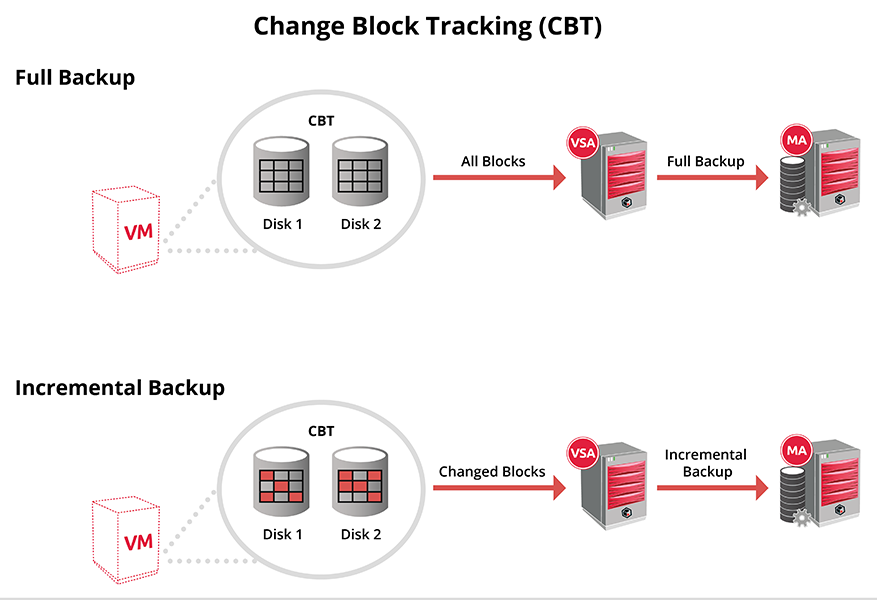
Enable Changed Block Tracking (CBT) to optimize incremental backups of virtual machines by reading only the allocated and modified portions of virtual disks. Incremental backups can use Commvault CBT, native Microsoft CBT, or Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC):
-
For Hyper-V virtual machines running on Windows Server 2012 R2 editions, Commvault CBT enhances backup performance of VHDX-format disks.
The Commvault CBT mechanism is provided as a CVCBT driver along with the Virtual Server Agent (VSA) software. If CBT is enabled and if both the VSA proxy and the virtual machine proxy are running on a Windows Server 2012 R2 node, Commvault changed block tracking is used. The driver is supported on all editions of Windows Server 2012 R2 (Hyper-V Core, Standard and Datacenter editions). The VHDX files can reside on local volumes, cluster shared volumes, or SMB shares. CBT is not supported for backups on remote SMB (Server Message Block Protocol) shares.
-
Backups of VHD-format disks and virtual machines running on Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows Server 2012 continue to use the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) mechanism to back up the parts of virtual disks that have changed since the last full backup. With CRC, the amount of data that is transferred to the MediaAgent is less, but the backup operation must read and compute the CRC checksum against all disk blocks. The time required for the disk I/O operations increases the total time of incremental backups to nearly as long as full backups.
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 and Later Versions
-
For Windows Server 2016 or later, Commvault CBT uses Microsoft's Resilient Change Tracking (RCT) feature to track changed blocks on the virtual disks.
-
For virtual machines running in a Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V cluster, the use of checkpoints for backups simplifies the backup process. For each virtual machine, the backup takes a checkpoint that includes only that virtual machine. Once the backup is completed, the checkpoint is converted to a reference point with a unique ID and saved with the backup. Changed block tracking uses the reference point to identify changes since the last backup. The reference point is retained until the next backup is completed and a new checkpoint is generated.
-
In a mixed mode cluster where some nodes have not yet been upgraded from Windows Server 2012 R2 to Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2016 operations are not supported until all nodes in the cluster are upgraded to 2016 and the functional level of the cluster is switched to Windows Server 2016 mode. Backups and restores use the same processes as Windows Server 2012 R2. With this, the behavior of changed block tracking varies:
-
If both the VSA proxy and the virtual machine proxy are running on a Windows Server 2012 R2 node, Commvault changed block tracking is used. Otherwise, incremental backups use the VSS backup method with CRC for changed block tracking.
-
If a virtual machine fails over from a Windows Server 2012 R2 node to a Windows Server 2016 node, incremental backups use the VSS backup method with CRC for changed block tracking. If the virtual machine fails back to a Windows Server 2012 R2 node, CBT resets and the next incremental backup includes all of the virtual machine data (equivalent to a full backup).
-
-
In a new Windows Server 2016 cluster, virtual machines are version 8 or later. In a cluster that has been upgraded to Windows Server 2016, virtual machines using older versions can still run, but cannot use all Windows Server 2016 host features. For example, all virtual machines running on a Windows Server 2016 node must be upgraded to version 8 or later before they can use Windows Server 2016 changed block tracking. In a Windows Server 2016 node that includes older version VMs, incremental backups include all of the virtual machine data (equivalent to a full backup).
-
To validate Native Microsoft Changed Block Tracking successfully, you must specify a host installed with Microsoft Windows 2016 (or a later version) as the backup copy host. You can use older operating systems to perform backup copy operations, but traditional cyclic redundancy check (CRC) backups are performed during incremental backup jobs.
For instructions on enabling or disabling CBT, see Enabling or Disabling Changed Block Tracking.
How Commvault CBT Works
The CVCBT driver is available with the software on each Hyper-V node in a cluster. After enabling CBT backups, when you run the first backup of a CBT enabled subclient, the CVCBT driver is activated and starts tracking the changed blocks on the virtual disks for the given virtual machines. The CBT driver monitors the virtual disks and maintains a bitmap (.cvf) file of the blocks that have changed. During subsequent incremental backups, these bitmap files are read and only the changed data blocks are backed up.