An unplanned failover can be performed in the event of a disaster, such as the following:
-
When the production CommServe host is inaccessible due to network or hardware failure
-
When the production CommServe host is partially available
-
When there is a failure during a planned failover
Caution
Unplanned failovers can cause data loss, especially if a LiveSync operation is not performed before failing over to the standby CommServe. Use extreme caution while performing unplanned failovers. Use the following steps to perform the failover. Do not manually perform additional steps to initiate the failover.
Procedure
-
Perform the following steps, if the production CommServe host is available:
-
Login to the production CommServe host.
-
If the CommServe is currently in a "lockdown" mode where client certificate authentication is forced during installation, reset the CommServe lockdown by setting the Force per-client certificate authentication option to No from the CommCell Console > Control Panel > Certificate Administration dialog box. (This setting can be re-enabled once the failover is completed.) For more information on client certificates, see Client Certificates - Enforcing Authentication of Client Certificates during Installations.
-
Shut down the services associated with both the CommServe and the SQL client in the production CommServe host.
-
-
Login to the standby CommServe host.
-
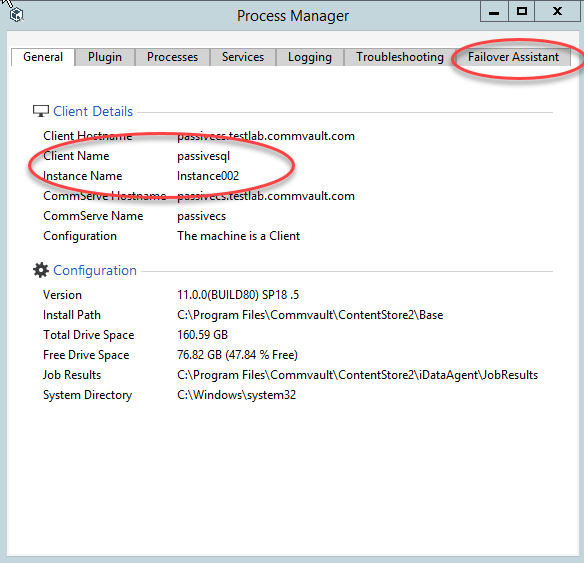
Open the Process Manager associated with the SQL client.
Tip
The SQL client will have the Failover Assistant tab as shown in the following sample image.
-
On the Failover Assistant tab, select the following options:
-
From the Failover To list, click the name of the passive node that must be used for performing the failover.
-
From the Failover Type list, click Production.
-
-
Click Initiate Failover.
-
On the Confirm prompt, type confirm and click Ok.
Note
For unplanned failovers, it may take a few minutes for the failover process to start, as the process checks whether the SQL nodes are reachable.
Result
-
The failover is initiated and the sequence of tasks performed during the process is displayed in the Process Manager window.
-
A DDB Resynchronization job will also be automatically initiated after the failover.
Caution
If there is a failure during an unplanned failover, contact Commvault Customer Support. Do not perform any manual or additional steps to recover from the failure.
What to Do Next
-
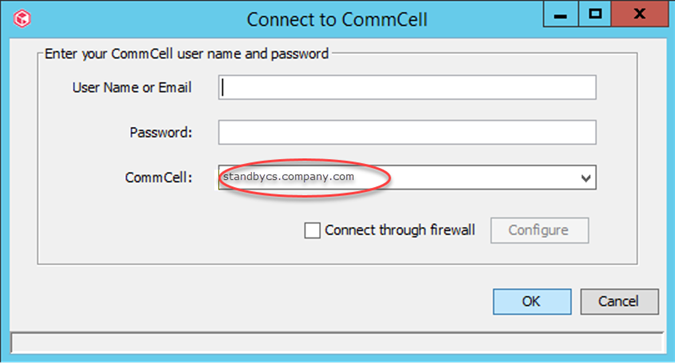
If a floating CommServe name is not used, make sure to open the CommCell Console and/or Command Center from the new active CommServe host, after a successful failover. Make sure to connect to the currently active host in the CommCell box displayed in the Connect to CommCell dialog box.
-
If you have failed over to a CommServe host located in a Cloud, or behind a firewall where port 8401 (GxEvMgrS port) is not reachable, make sure to enable the Connect through firewall option, click the Configure button, and then specify the proxy computer details in the Proxy hostname or IP address and Proxy port number boxes. Ideally this proxy computer must be a standalone computer which is accessible to both the CommServe host and the clients.
-
If client certificate authentication during installation was disabled before the failover, set the Force per-client certificate authentication option to Yes from the CommCell Console > Control Panel > Certificate Administration dialog box. For more information on enabling this option, see Enabling Client Certificate Authentication on the CommServe Computer.
Post Failover Tasks for a CommServe Using A Floating CommServe Name
Perform the following steps after a failover:
-
Update DNS to re-point the floating CommServe name to the IP address of the standby CommServe host. For information on changing the IP address, refer to the documentation associated with DNS software implemented in your environment.
-
Test and verify that the floating CommServe host resolves to the IP address associated with the standby CommServe host using
pingor the equivalent network command.For additional information about setting up and using floating CommServe name, see Setting Up Failovers Using A Floating CommServe Name.
-
If you have data Interface Pairs (DIP) defined, make sure that the floating CommServe name or IP address of both production and standby nodes are used to configure multiples DIP routes.
For more information about setting up DIPs, see Configuring a Dedicated Backup Network Using Data Interface Pairs.
Additional Notes
-
If necessary, suspend all schedules after an unplanned failover so that jobs are not started right away.
-
After an unplanned failover, ensure that the original CommServe is setup as the standby, as follows:
-
If the original production CommServe host can be restarted, restart the CommServe and verify that this CommServe is set as the Passive node in the Process Manager. For more information about verifying the node, see the Process Manager section in Verifying the Default Setup.
-
If the original production CommServe host cannot be restarted, setup a new standby CommServe host. For more information about setting up a standby CommServe host, see Reinstalling the Standby CommServe Host.
-
Once the CommServe is setup, verify and ensure that the LiveSync Operation is run from the currently active CommServe host to the standby CommServe host before performing another failover.
-
Related Topics
-
Planned failovers can be performed to alternate between the active and passive CommServe hosts. For more information, see Planned Failovers.
-
Test failovers can be performed to test the failover process and to verify that the services are successfully started in the standby CommServe host after a failover. For more information, see Verifying Disaster Readiness.
-
Maintenance failovers can be performed to install the Commvault Feature Release on the CommServe hosts. For more information, see Installing Service Packs On High Availability CommServe Host Setup.