The Advanced section describes the steps that advanced users must follow to virtualize the client computers using the CommCell Console.
Creating a Virtual Machine Using a Point-In-Time Backup
By default, the latest data and configuration settings of the client computer, backed in the default backup set, is used to create the virtual machine. However, you can create the virtual machine with data and configuration settings that was backed up at any point in time.
Follow these steps to select the point in time.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
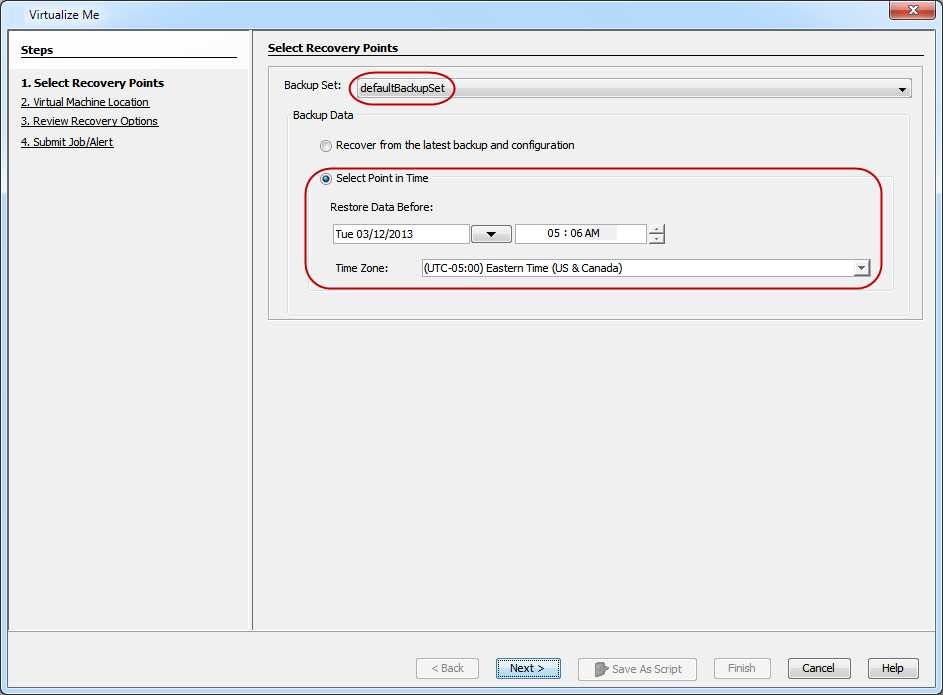
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Select Point in Time.
-
Select a date and time to specify the point in time. All of the data that was backed up before the specified point in time is restored when the virtual machine is created.
-
The default time zone of the CommServe is used to determine the point in time. If you want to restore data that was backed up in a different time zone, select the required Time Zone.
-
Click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
Creating a Virtual Machine Using a User Defined Backup Set
By default, the latest data and configuration settings of the client computer, backed in the default backupset is used to create the virtual machine. You can create a backupset to back up data and configuration settings for the Virtualize Me operation. This is useful when you want to back up only selected data on the client computer and create a virtual machine with the selected data.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
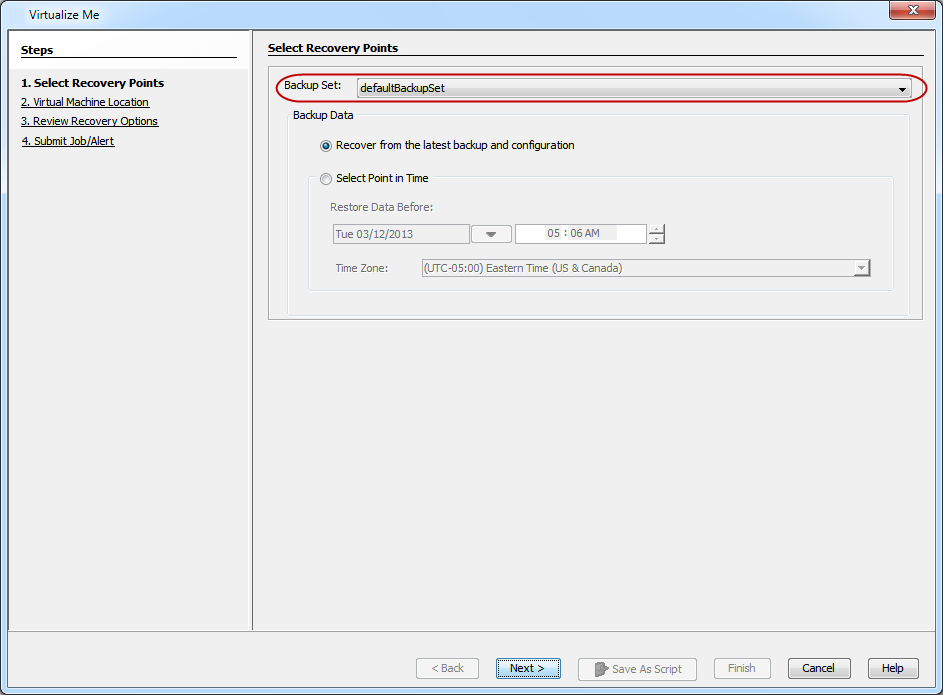
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, select a <Backup Set> from the Backup Set list.
-
Click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
Firewall Settings for Virtualize Me Clients
Firewall Configuration
Firewalls provide security by blocking unauthorized access to networked computing and communications resources. Internet Protocol (IP) ports are configured in firewalls, permitting specific kinds of information to flow to and from opened IP address:port combinations, in specific directions (in, out or both). Firewall functionality is most often provided by either a stand-alone network appliance, or firewall software running on a general-purpose computer.
Commvault provides additional network protection for the Commvault application software, which you configure from the CommCell Console.
-
Choose one of the following methods to configure network routes on the CommServe computer depending on your requirement:
-
Perimeter Network Using Commvault Network Gateway (also known as a DMZ)
-
Create a Client Computer Group and add the Virtualize Me clients to the <Client Computer Group>.
-
On the CommCell Browser, right-click the CommServe and click Properties. The CommCell Properties dialog box appears.
-
In the CommCell Properties dialog box:
-
Click the Network Route Configuration tab and click the Configure Network Route Settings check box.
-
Click Add. The Connections to CommServe dialog box opens.
-
In the Connections to CommServe dialog box:
-
In the From box, select the newly-created client group.
-
In the To box, select Restricted.
-
Click OK.
-
-
Click OK.
-
-
Right-click the Client Computer Group and click Properties. The Client Group dialog box opens.
-
In the Client Group dialog box:
-
Click the Network Route Configuration tab, click the Configure Network Route Settings check box, and click Advanced. A Warning dialog box is displayed.
-
Click OK on the Warning dialog box and click Add. The Connections to Client_Group_Name dialog box appears.
-
In the Client_Group_Name dialog box:
-
In the From box, type or select a client or client group that has restrictions to communicate with the CommCell entity.
-
In the To box, select Restricted.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Recovery
If you have network routes configured between the client and the CommServe, in the Client Group Name box, type the name of the client computer group that you created with the configuration and click Next.
Limitations
-
During One-Way direct network route configuration, only the client can initiate a connection with a CommServe.
-
During Network Gateway in a Perimeter Network configuration, the network gateway computer can alone initiate a connection.
-
In the Certificate Administration dialog box, Force per-client certificate authentication on CommServe option must be set to No. If the option is set to Yes, the firewall configuration will not work.
-
If you have Data Interface Pairs (DIPs) configured on your CommCell, make sure that you remove them. For instructions, see Deleting Data Interface Pairs.
Choosing a Different Backup Copy for Virtualization
You can use a specific copy of the backup data to create the virtual machine. By default, the virtual machine is created with the backup data from the storage policy copy that has the lowest copy precedence. Follow these steps to specify the copy precedence of the backup copy.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
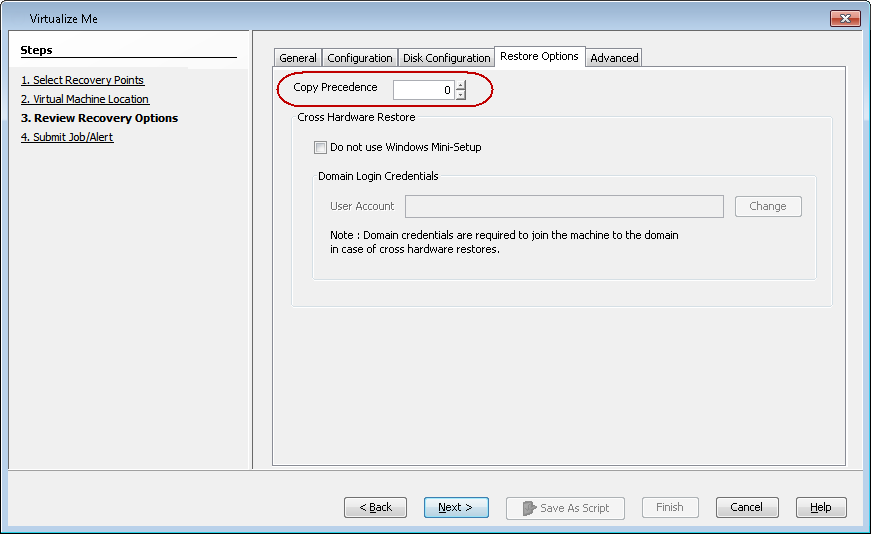
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Restore Options tab.
-
Enter the Copy Precedence of the copy that you want to use to create the virtual machine.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
Using an Alternate User Account for Virtualization
By default, the user account that you used to log into the CommCell Console is used to perform the virtualization job. However, if you use the Active Directory User account to log into the CommCell Console, you must enter the password for the user account. If you logged in as the CommCell Console administrator, you do not need the password to perform the virtualization job.
The Administrator can create a separate user account to perform the virtualization job. This user account must have appropriate permissions to perform a Virtualize Me operation. For more information on the required permissions, see User Security Permissions and Permitted Actions by Feature.
If you want to use an administrator account to perform the virtualization job, follow these steps.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
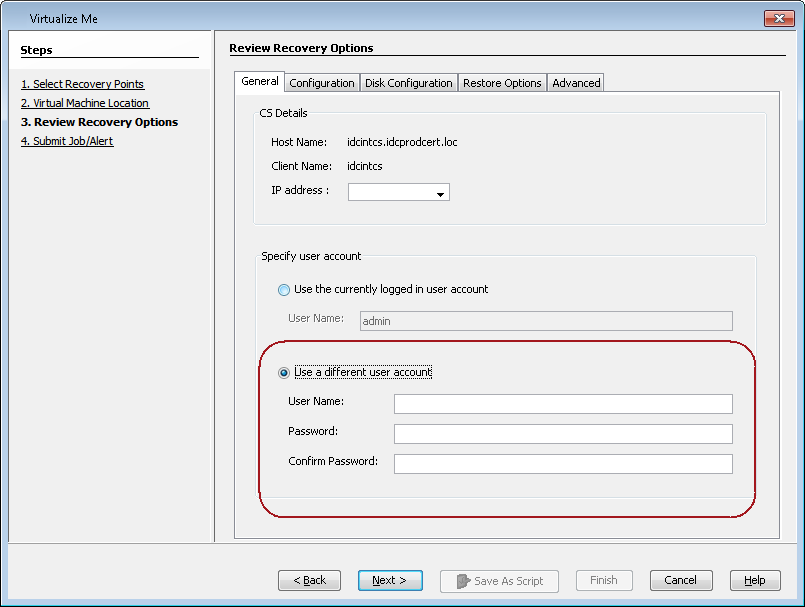
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click Use a different user account.
-
Enter the credentials for the user account which you want to use to perform the virtualization job.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
Scheduling the Virtualization Operation
Scheduling jobs help to ensure that certain operations are automatically performed on a regular basis without user intervention. Follow these steps to schedule the virtualization of a physical machine.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click Next.
-
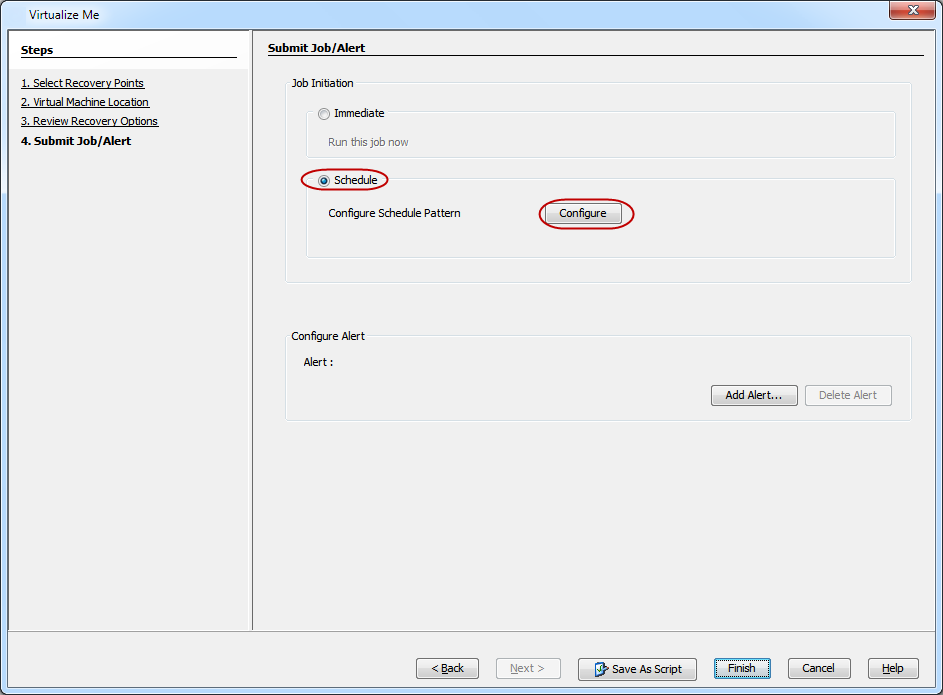
On the Submit Job dialog box, click Schedule and then click Configure.
-
Select the appropriate scheduling options.
-
Click OK to close the Schedule Details dialog box.
-
Click Finish.
Setting Up Alerts for the Virtualization Operation
You can set up alerts for a Virtualize Me job from the CommCell Console. If the Virtualize Me job starts or fails or completes with errors, the configured users will receive an alert notification.
For details about alert criteria, refer to Available Alerts.
Follow these steps to configure alerts for a Virtualize Me job.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click Next.
-
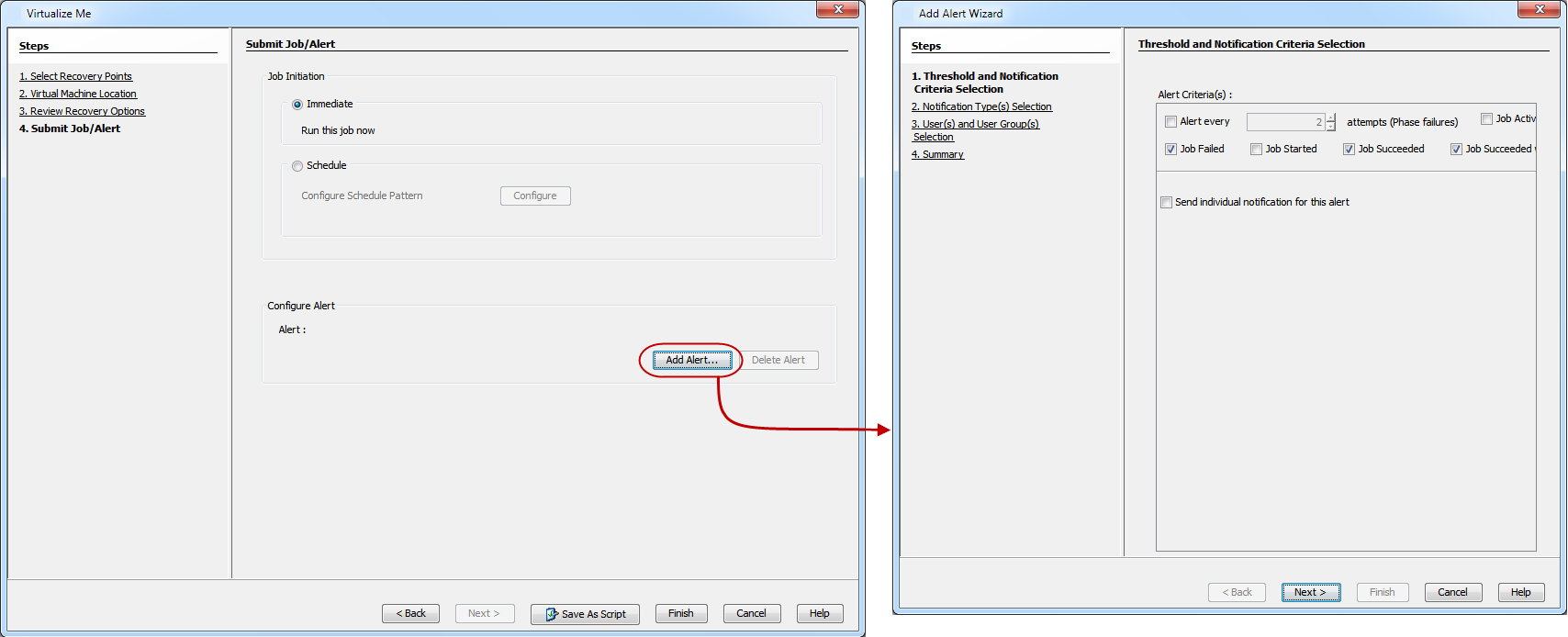
On the Submit Job/Alert dialog box, click Add Alert....
-
From the Add Alert Wizard dialog box, select the threshold and notification criteria, and then click Next.
-
Select the way in which the alert is to be sent to its intended recipient, and then click Next. For example, you can click Select [Email] for notification to send the alert as an email.
-
Select the CommCell users and/or user groups that will receive the alert, and then click Next.
-
Review the options that you selected in the Summary tab, and then click Finish.
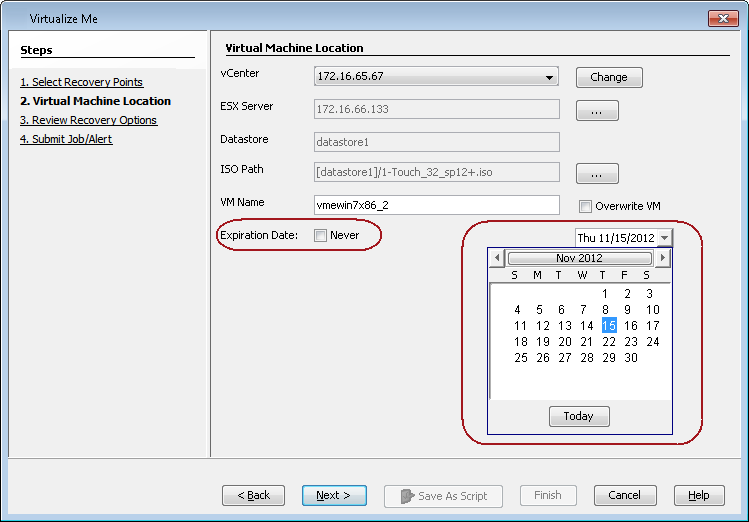
Setting an Expiration Date for the Virtual Machine
You can set an expiration date for the virtual machine. Follow these steps to set the expiration date of the virtual machine.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Clear the Never check box next to Expiration Date, and then select an expiration date from the calendar.
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click Next.
-
Click Finish.
After the expiration date, the virtual machine is powered off and decommissioned. However, if you have performed regular backups of the virtual machine using the Virtual Server iDataAgent, you can recover a decommissioned virtual machine at any time. We recommend that you use the Virtual Server iDataAgent to perform regular backups of the virtual machine.
You can use the VM Lifecycle management feature to change the expiration date later. For more information about how to set up this feature, refer to VM Lifecycle Management Administrator Overview.
Once you set up the VM Lifecycle management feature, refer to Renew a Virtual Machine.
Modifying the Configuration for a Virtual Machine
When you convert the client computer into a virtual machine, you can modify the disk configuration of the client computer so that the virtual machine is created with the modified disk configuration.
Select the Volumes
Select specific volumes on the client computer. You can select only system volumes and then add the non-system volumes later. This feature is useful in the following scenarios:
-
The non-system volumes reside on disks provisioned by iSCSI or SAN.
-
The non-system volumes contain large data and the ESX server does not support large disks.
-
You do not want to restore the data from the non-system volumes.
Follow these steps to select disks on the client computer.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the SelectRecoveryPoints dialog box, click Next.
-
On the VirtualMachineLocation dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the ReviewRecoveryOptions dialog box, click the Restore Options tab.
The list of volumes that are on the client computer appears. You can also view disk information at the bottom of the volume list.
-
Select the required volumes from the list. The virtual machine is created with the Selected volumes.
When all of the volumes on a disk are selected, the disk is selected automatically.
If you clear a disk, all of the volumes on the disk are cleared automatically.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
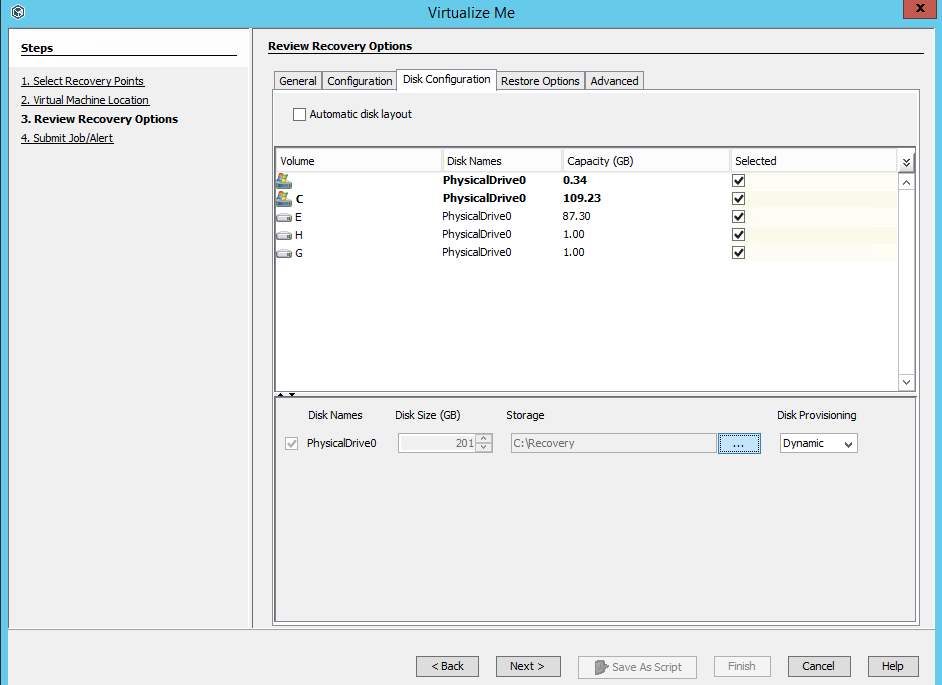
Modify the Volume Size and the Disk Size
You can increase or decrease the volume size for all of the non-system volumes on the client computer. You can also increase the disk size for all of the disks of the client computer.
Note: When performing a recovery from block-level backups, you cannot decrease the volume size because the destination volume cannot be smaller in size than the source volume.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Disk Configuration tab.
The list of volumes that are available on the client computer is displayed. You can also view physical drives for each volume.
-
Select the required volumes from the list. The virtual machine is created with the Selected volumes.
-
Click in the Capacity column, and then enter the volume size for each volume.
If you decrease the volume size, make sure that the volume size is greater than the actual data size on the volume.
If you select the Automatic Disk Layout check box, the disk size increases automatically when you increase the volume size. You can also increase or decrease the disk size manually.
Ensure that the disk size is greater than the size of all the volumes on the disk.
The disk size is equal to the size of all of the volumes on the disk.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
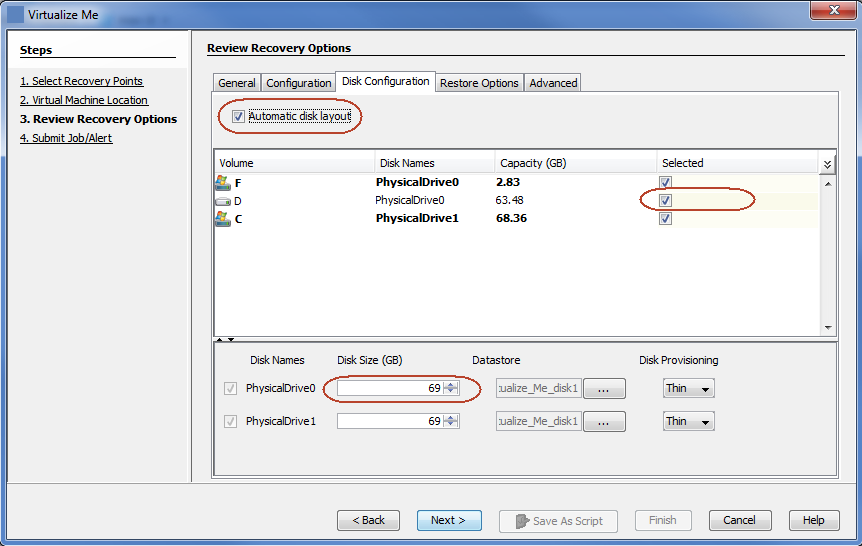
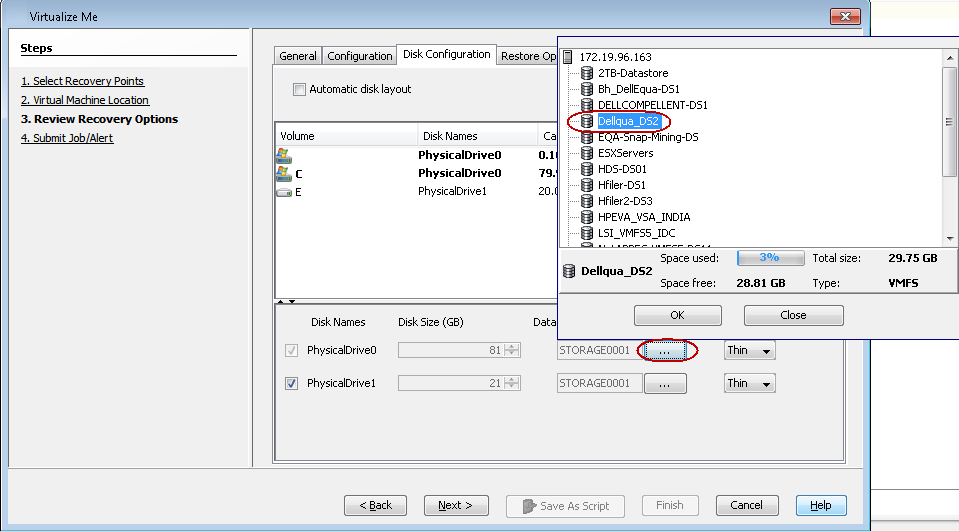
Select a Datastore
When you create a virtual machine, all of the disks are created in the default datastore automatically. The default datastore is the datastore that you specified in the Virtual Machine Location dialog box.
You can select a different datastore for a disk. All of the volumes on the disk are created in the selected datastore.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Disk Configuration tab.
The list of volumes that are available on the client computer appears. You can also view disk information at the bottom of the volume list.
-
Select the required volumes from the list. If you do not select any volume from a disk, the disk is not selected.
The list of disks displays the datastore where the disks are created.
-
Click
 to select a Datastore.
to select a Datastore. -
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
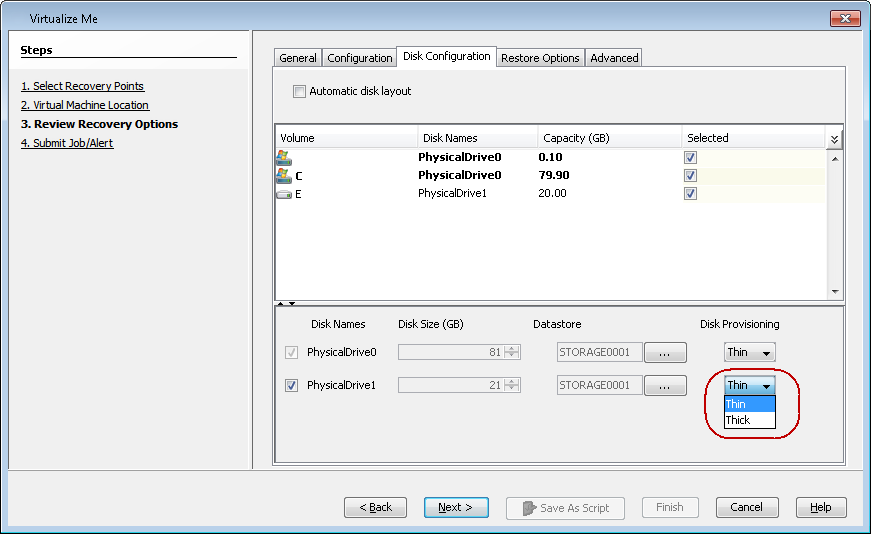
Configure the Disk Provisioning
By default, thin provisioning is used for disk space allocation for all disks. You can configure disk provisioning for each disk.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Disk Configuration tab.
The list of volumes that are available on the client computer appears. You can also view disk information for each volume at the bottom of the volume list.
-
Select the required volumes from the list. If you do not select any volumes from a disk, the disk is not selected.
-
Select Thin or Thick disk provisioning for the selected disks.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
Modify the Network Configuration
When you convert a client computer into a virtual machine, you can modify its network configuration such as IP address, default gateway, and so on.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Configuration tab.
-
Select the network configuration, and then click Edit.
-
Modify the IP address or any other network configuration details.
Click Use DHCP if you want to use a dynamic IP address instead of a static IP address.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
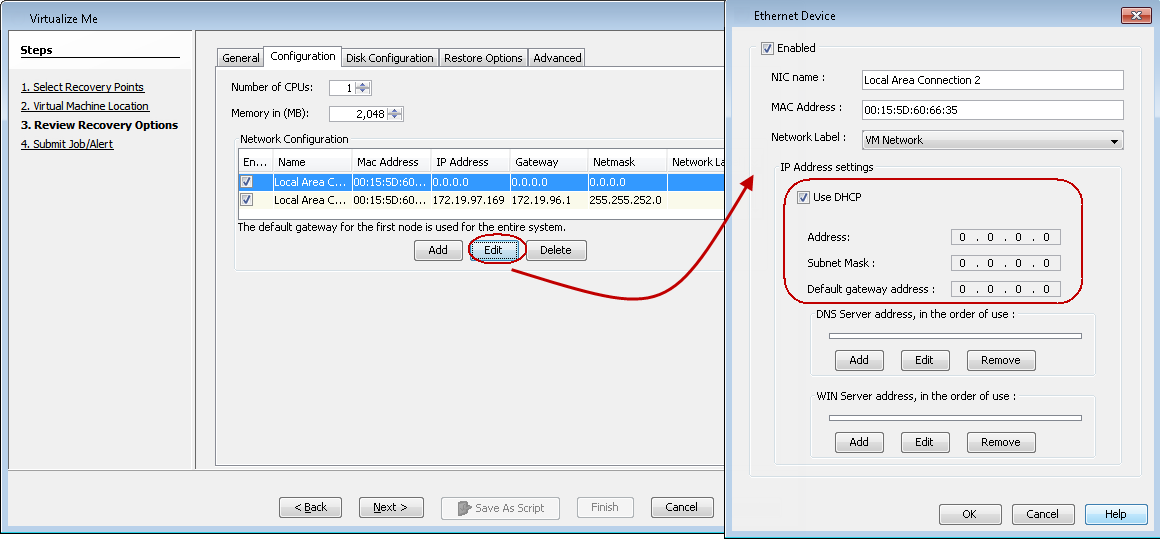
Configure the WINS or DNS
When the client computer and the CommServe are in the same domain, the DNS (Domain Name System) is used for name resolution between the client computer and the CommServe.
WINS(Windows Internet Name Service) is used for name resolution when:
-
The CommServe and the client computer are in different networks.
-
The CommServe is registered in a workgroup.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Configuration tab.
-
Select the network configuration, and then click Edit.
-
Do either of the following:
-
If you want to use DNS, click Add in the DNS Server address area, and then enter the IP address of the DNS Server.
-
If you want to use WINS, click Add in the WINS Server address area, and then enter the IP address of the WINS Server.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
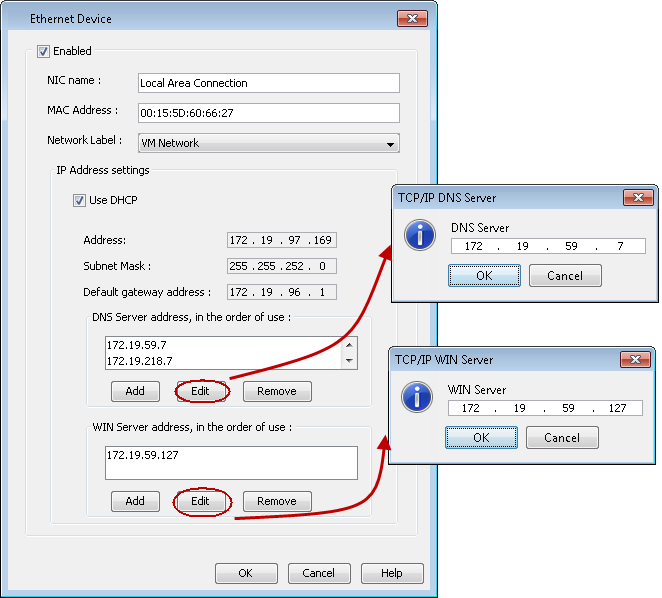
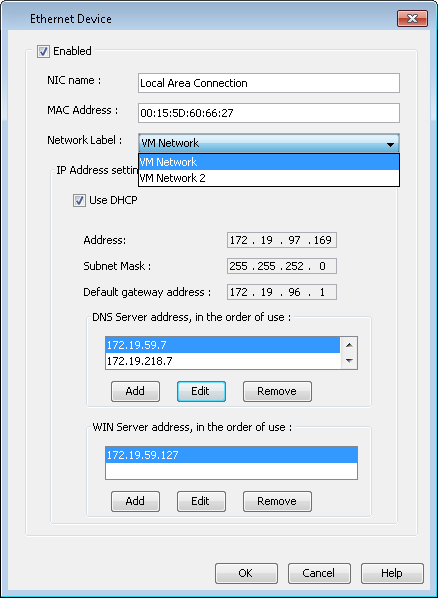
Assign a Network Label
Virtual Center uses labels to identify the virtual network adapter that is associated with a physical network. If you want to associate the network adapter of the VM with a specific virtual server network, follow these steps.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Configuration tab.
-
Select the network configuration, and then click Edit.
-
Select a network label from the Network Label list. This list displays all of the network labels that are available on the ESX server or the vCenter.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
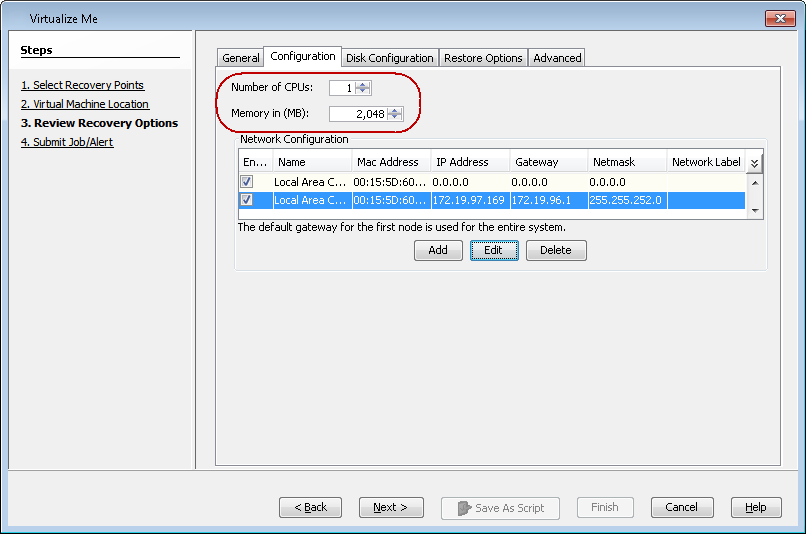
Modify the Memory
When you convert the client computer into a virtual machine, you can increase or decrease its memory size.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Configuration tab.
-
In the Memory in (MB) box, increase or decrease the size of the memory.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
Modify the Number of CPUs
When you convert the client computer into a virtual machine, you can increase or decrease the number of virtual CPUs.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the Select Recovery Points dialog box, click Next.
-
On the Virtual Machine Location dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Review Recovery Options dialog box, click the Configuration tab.
-
In the Number of CPUs box, increase or decrease the number of CPUs.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.

Skip Installing Drivers from the Windows Cache
When you convert the client computer into a virtual machine, the hardware configuration of the computer might change. For example, the NIC card, Network Adapters, SCSI Adapters, Floppy Drive, and so on.
In this case, the Windows Mini-Setup process runs automatically after the Full System Restore. This process installs the drivers that are available in the local windows cache.
Important: If you rename the administrator account on the source computer, then, after a Virtualize Me operation that contains the Mini-Setup (SysPrep) components, the user account on the destination computer is automatically renamed to the original name. After restarting the computer, you can log on to the destination computer using the same credentials that you used on the source computer for the renamed account.
If you are not modifying the hardware configuration, you can skip the Windows Mini-Setup process. Follow these steps if you do not want to install any drivers after the full system restore.
-
From the CommCell Console, navigate to Client Computers.
-
Right-click the <Client>, point to All Tasks | Virtualize Me, and then click <Agent>.
-
On the SelectRecoveryPoints dialog box, click Next.
-
On the VirtualMachineLocation dialog box:
-
For VMWare, select a vCenter, ESX Server, and a Data Store. Specify the ISO Path on the ESX server.
-
For Hyper-V, select an Hyper-V instance, Hyper-V Host, and a location for the virtual machine in the Storage box. Select the location for the ISO Path on the Hyper-V server.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the ReviewRecoveryOptions dialog box, click the Restore Options tab.
-
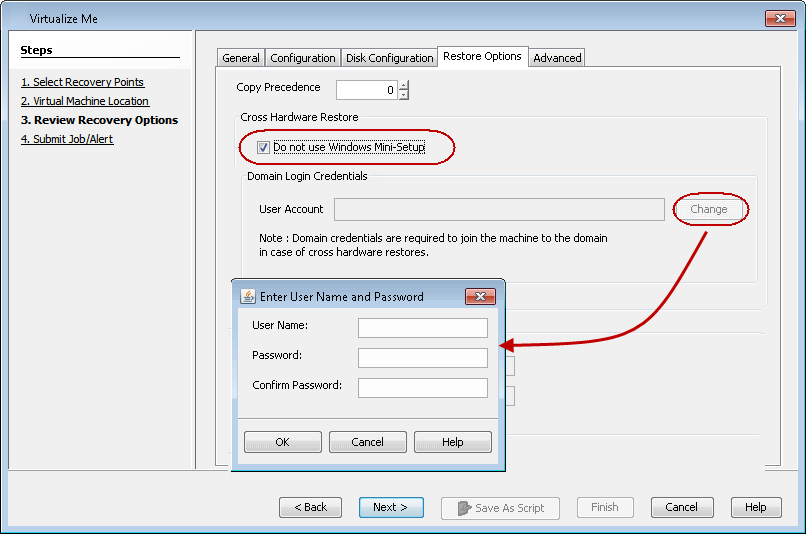
Select the Do not use Windows Mini-Setup check box.
Click OK on the warning message.
If you perform the cross hardware restore and skip the Windows Mini-Setup process, the client might become unstable after the restore completes.
-
If the client computer is member of a domain, click Change, and then enter the credentials of the domain where you want to add the virtual machine.
If your client has a Windows 2003 operating system, enter the License Key.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
Related Reports
Job Summary Report
You can use the Virtualize Me Job Summary Report to review information that is related to all of the Virtualize Me jobs that are run in the CommCell during the specified time period. This report is useful if you need information about:
-
All Virtualize Me jobs with a specified status during a specified time period
-
The user who set up the job
-
The client for which the job run
-
The failure reasons, if applicable
-
From the CommCell Browser, right-click the CommServe node, point to View, and then click Admin Job History.
The Admin Job History Filter dialog box appears.
-
From the Job Type list, select Virtualize Me.
-
Click OK.