Cloud Assembly allows you to select and assemble all of the resources intended to be protected and recovered.
Azure Cloud Assembly Creation
To create a new Azure Cloud Assembly in Cloud Rewind, complete the steps shown below.
General Information
-
Enter the Cloud Assembly name and description.
-
Select the Cloud Connection for which the resources have to be protected.
-
Choose the desired primary region from the list of operational regions, and specify the Resource Group details of the primary region.
-
For cross-region recovery, enable "Allow cross-region recovery" option.
-
Select the desired recovery region from the list of operational regions, and specify the Resource Group details of the recovery region.
Resources
-
Choose the resource group to be protected.
-
You can protect all resources within the resource group using entire resource group option, or you can enable protection based on resource tag using select using tags option.
-
If you are planning to protect only the storage account, enable the 'Protect Storage Account Only' option.
-
You can exclude specific resources from protection by using the 'Exclude Resources with Following Tags' option.
Protection Strategy
-
Provide a backup resource group for both the source and destination regions to store your data backups.
-
For storage account protection, a recovery storage account needs to be mapped as a prerequisite. Click here to learn more.
Protection Policy
-
Select a protection policy to protect the resources.
-
Protection policy can be used to define the time at which the snapshot has to be taken and the number of snapshots to be retained using a retention count.
-
A policy template can be created to fit the protection needs best.
-
To create a new protection policy template, click here.
-
The policy can be activated as by the scheduled policy, immediately triggering one policy or by delaying to the specific time.
Review
-
Review the general information, resource information, and the protection policy details provided.
-
Edit the details if required and proceed to finish and create a Cloud Assembly.
Actions
Once an Azure Cloud Assembly is created, you can find the following actions in the upper right corner:
-
Edit: In the Cloud Assembly Edit section, users can modify the cloud assembly's name and description under General Information. Additionally, users can update the recovery region and enable cross-account functionality as required. They can also adjust resource protection options and the protection strategy under the Resources and Protection Strategy sections, respectively.
-
Recovery Profile: Users can create different recovery profiles with different recovery configuration using this option. This functionality streamlines the selection of recovery templates based on specific needs.
-
Disable: The Disable option allows users to temporarily disable cloud assembly protection, which can be re-enabled as needed. (Disable option is restricted for storage account-only assemblies).
-
Configuration: In the webhook section, users can set up custom automation scripts using the webhook options. Webhooks are HTTP/HTTPS callbacks that can be triggered pre- or post-recovery or post-reset. Click here to learn more about webhooks.
-
Config Drift: This option effortlessly compares two or more protection timelines, enabling users to identify configuration differences between them.
-
Delete: The Delete option permits users to permanently remove the cloud assembly from the system.
Ad Hoc Backups
Cloud Rewind offers ad hoc backup capability for Azure, enabling users to trigger an immediate protection action outside of the scheduled backup cycle. Ad hoc backup provides flexibility by enabling immediate, policy-driven protection for Azure workloads, ensuring that business-critical workloads can be protected instantly when required. This feature allows enterprises to safeguard workloads while maintaining governance and consistency across multiple cloud environments.
Key benefits:
-
On-demand backups complement scheduled protection.
-
Policy-based retention ensures consistency.
-
Concurrency checks prevent conflicts with in-progress protection jobs.
Ad hoc backup is available through the following:
-
Cloud Assembly Actions (initiate backup directly on a selected assembly).
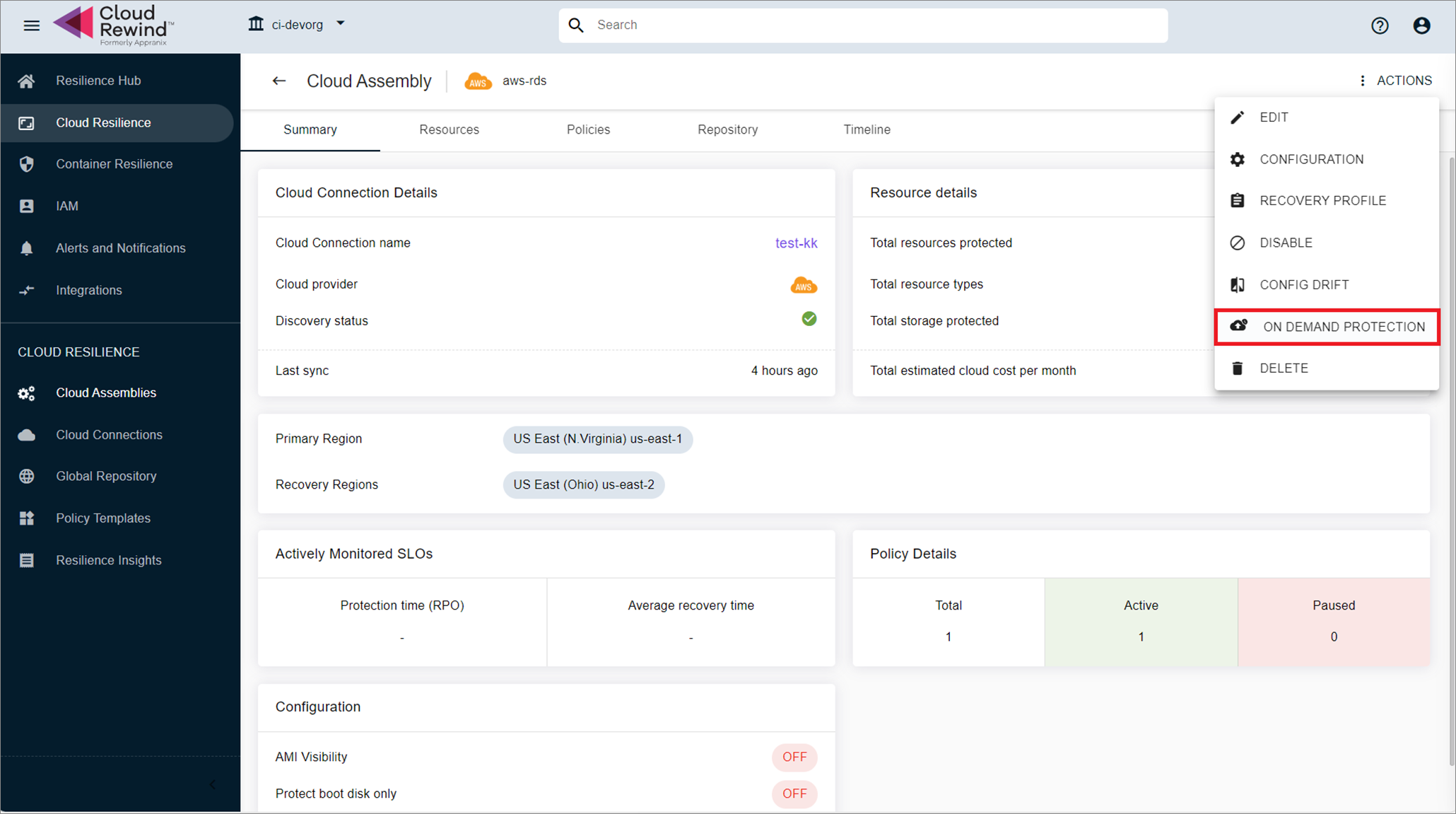
-
Protection Policy Actions (trigger backup based on an existing policy attached to the assembly.
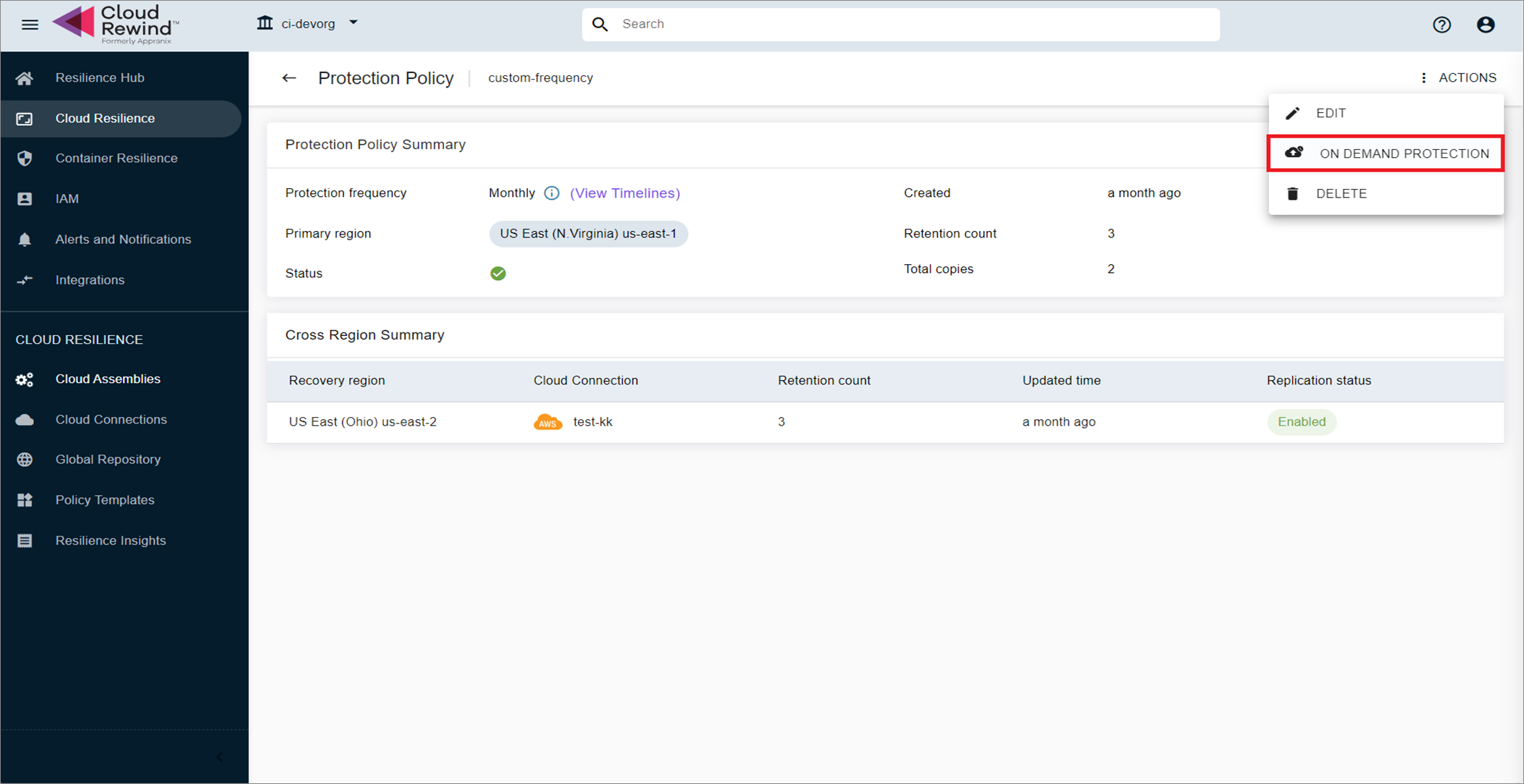
How Ad Hoc Backup Works
-
Policy Selection
-
If multiple protection policies exist for a Cloud Assembly, the user must select the appropriate policy to initiate the ad hoc backup.
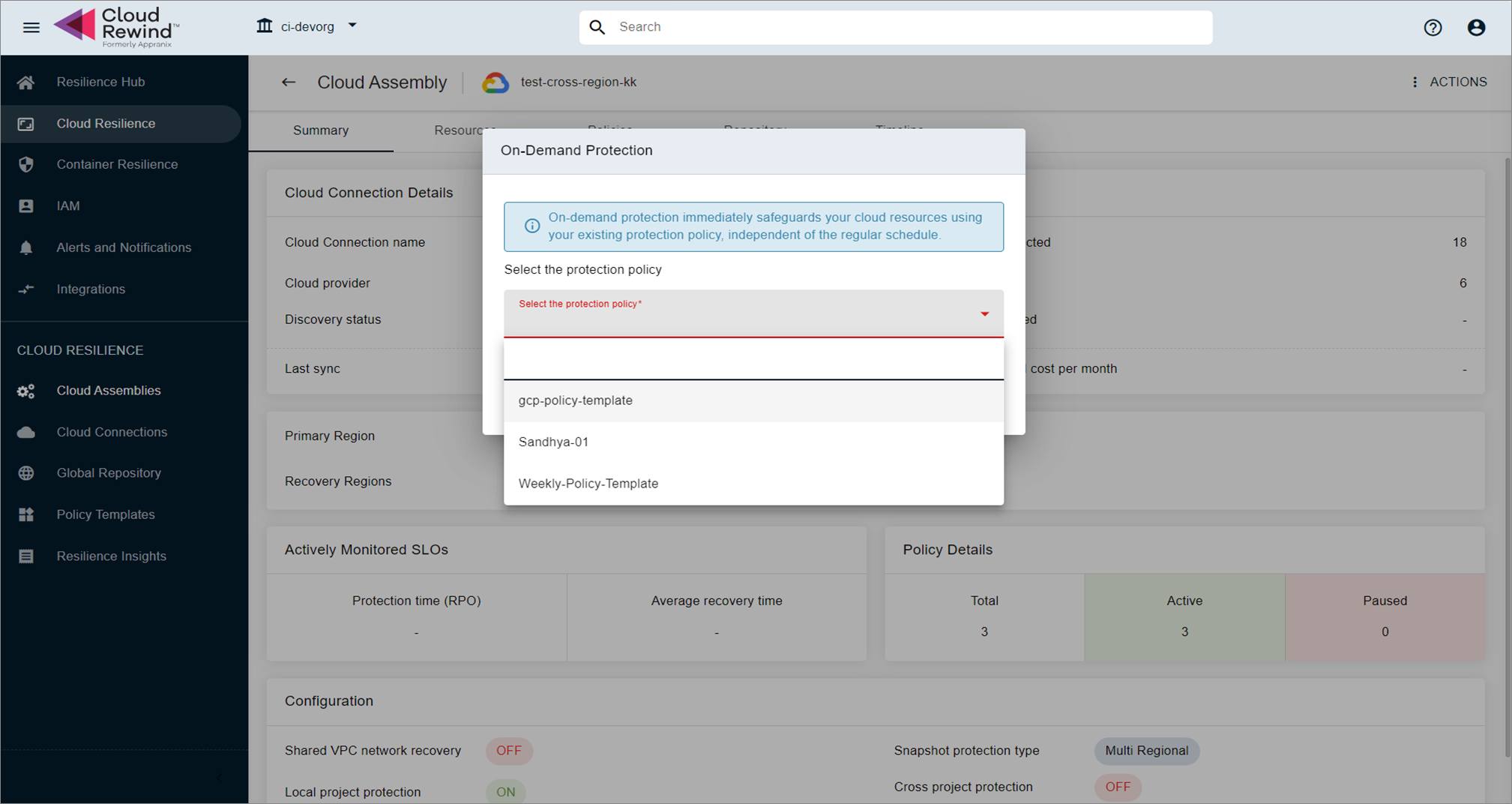
-
The backup will follow the retention rules of the selected policy (retention count applied as per policy configuration).
-
-
Execution
-
Once triggered, an ad hoc backup behaves like a scheduled protection job, creating a recovery point consistent with the selected policy.
-
The backup is logged and tracked in the Cloud Rewind job execution history.
-
Constraints and Limitations
-
Concurrency Restriction:
- If a scheduled backup or an ad hoc backup job currently is in progress for the same protection policy, an ad hoc backup cannot be triggered.
-
Policy Dependency:
-
An ad hoc backup requires an existing protection policy.
-
An ad hoc backup cannot be initiated without selecting a valid policy.
-
-
Retention Enforcement:
- An ad hoc backup is subject to the retention count defined in the selected policy. Older backups will be pruned according to standard policy retention rules.