Restore your backed up data to the original location on the same computer by using the default values in the Restore Options dialog box. Optionally, you can choose different combinations of restore options to perform different types of restores. To determine which combination of options is required to meet your needs, refer to the Restore Options section.
If you want to find and restore specific data, see Find. To perform a restore operation by using the command line interface, see Browsing Backed Up Data for Windows File System Agent.
About This Task
By default, when you perform a restore operation, the data is restored in place.
If the version of the backed up file is newer than the one that exists on the destination, the destination file is overwritten.
If the version of the file on the destination is newer, then the backed up file is not restored. The file is skipped during the restore operation. If necessary, you can restore the file out-of-place or rename it during restore.
You cannot directly restore a file or a folder that has special characters, such as square brackets([ ]) in its names. You can restore the parent directory in which these files or folders reside.
When you perform an in-place restore, Commvault software skips overwriting files to the Log Files folder, Base folder, and the GUI folder. If you want to restore specific log files to troubleshoot issues, perform an out-of-place restore of the Log Files folder.
Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2016 has a deduplication feature that can be enabled. Data from deduplicated volumes will be backed up in its original state (uncompressed). Therefore, during a restore, ensure that you have enough storage space on the volume to restore the full data size.
Before You Begin
-
Plan the configuration for the restore operations. After selecting the data that you want to restore, you will need to set the Advanced Restore Options for the restore operation. These provide tools to optimize the restores for specific circumstances. The most common advanced options are listed below:
-
General
-
Startup
-
Pre/Post
-
Copy Precedence
-
Data Path
-
Encryption
-
Alert
-
-
Decide whether you will run the restore immediately or on a schedule.
-
Determine whether you want to save your restore options as a script to run from a command line interface. To save your options as a script, you must define a schedule.
Procedure
-
From the CommCell Browser, expand Client Computers > client > File System > backup set.
-
In the right pane, right-click a subclient, and click Browse and Restore.
-
In the Browse and Restore Options dialog box, click View Content.
-
Select the data that you want to restore, and click Recover All Selected.
Note
Use caution when performing in place restores of selective content belonging to system drive (C:) as this can lead to inconsistent application or system itself.
-
On the Restore Option General tab, choose whether you want to run the restore job immediately or schedule it.
For more information about general restore options, see Restore/Recover Options (General).
-
On the Restore Option Job Initiation tab, choose how you want to initiate the restore jobs.
For more information about job initiation options, see Restore Options (Job Initiation).
-
Optional: To further customize the restore operation, click Advanced.
For more information about the Advanced Options, see Advanced Restore Options.
-
To determine which combination of options is required to meet your needs, refer to Restore Options.
-
Optional: To save the current backup options as a script file, click Save as Script.
For more information, see Command Line Interface.
-
Click OK.
If you selected to run the restore operation immediately, you can monitor the progress of your restore job from the Job Controller. If you chose to run the backup job according to schedule, the restore operation runs according to the schedule you defined. For more information, see Job Controller.
After the restore job is complete, you can view the restore job history. For more information, see Job History.
Restore Options
In-Place Restore to Overwrite Data Only if the Backed Up file is Newer
In-Place Restore to Overwrite the Existing Data
-
On the Restore Options - General tab:
-
Select the Overwrite Files check box.
-
Select the Unconditional Overwrite option.
-
Result
When the restore is complete, the destination file is overwritten.
In-Place Restore Only When the Data Exists On the Destination Computer
-
On the Restore Options - General tab:
-
Select the Overwrite Files check box.
-
Select the Restore only if target exists check box.
-
Result
Files on the destination are overwritten by the backed up version of files. However, files that are missing on the destination are not restored.
Rename the Files on Restore
-
On the Restore Options - General tab:
-
Select the Overwrite Files check box.
-
Select the Restore only if target exists check box.
-
Click Advanced.
-
On the Advanced Restore Options- Map dialog box, make the following selections:
-
Click the Map tab.
-
On the Map tab, in the Rename all restore files with suffix box, type the suffix that you want to append to the file name.
Note
The file is restored with a suffix only if the file name is already available on the destination folder. For example, if you are restoring a file with the name filename.txt and the file is already available in the destination folder, then the file is restored as filename_suffix.txt.
-
-
Result
Existing files on the destination are not overwritten by the backed up version and are restored with the appended suffix.
Out-of-Place Restore to a Different Folder on the Same Client Computer
-
On the Restore Options - General tab:
-
Clear the Restore to same folder check box.
-
Click Browse. In the Browsing for destination folderon <client> dialog box, select the folder where you want to restore your data, and then click OK.
-
Optionally, select Preserve Source Paths options to exclude files and folders from the source path.
-
-
On the Advanced Restore Options - Paths/Filters tab, exclude the following folders:
-
*:\drivers\*
-
*:\win*\inf\*
-
Note
Restores of symbolic link files are not supported
Examples:
-
If the selected data is Documents\Users\Memos\Sales, and you want to restore data only from the Sales folder, set the Preserve <n> level from end of source path option to 1.
-
If the selected data is Documents\Users\Memos\Sales, and you want to restore the data from Memos and Sales folders, set the Remove <n> level from beginning of source path option to 2.
Result
The files are restored to the destination folder that you specified. If the folder does not exist, a folder with the same name is created and the data is restored to that folder.
Out-of-Place Restore to a Different Client Computer in the Same CommCell
-
On the Restore Options - General tab:
-
In the Destination Client list, select the client. You can select any client that is in the same CommCell as that of the client from which the data was backed up.
-
To restore to the same folder on the destination, select the Restore to same folder check box. (Any existing data in that folder on the destination client is overwritten during the restore operation.)
-
-
On the Advanced Restore Options - Paths/Filters tab, exclude the following folders:
-
*:\drivers\*
-
*:\win*\inf\*
Note
If you restore a shared folder from one client computer to another client computer, the share status of the folder is restored.
Backed up data from clients running the current Commvault version cannot be restored to clients running older versions.
-
Out-of-Place Restores to the Cloud
You can use the Windows File System Agent to restore protected data from Windows or Mac computers to Microsoft OneDrive.
-
On the Restore Options - General tab:
-
In the Destination Client list, select the Microsoft OneDrive client that you configured. You can select any OneDrive client that is in the same CommCell.
For more information on configuring Microsoft OneDrive, see Configuration for OneDrive for Business.
-
Important: Irrespective of the restore options you choose, any existing data on the destination client is overwritten during the restore operation.
Note
Backed up data from clients running the current Commvault version cannot be restored to clients running older versions.
-
Cross-Platform Restore
You can restore data cross-platform to all supported versions of Windows, UNIX, Linux, and Mac. You cannot restore encrypted files from a Windows client to a UNIX client.
-
On the Restore Options - General tab:
-
In the Destination Client list, select a client in the same CommCell as the client from which the data was backed up.
-
Clear the Restore to same folder check box.
-
Click Browse. In the Browsing for destination folder on <client> dialog box, select the destination folder , and click OK.
-
Result
After the restore operation is complete, the data is restored to the destination folder that you specified in the Restore Options dialog box. If the folder you specified does not exist, a folder with the same name is created and the data is restored to that folder.
UNC Path or a NFS-Mounted File System Restore
-
On the Restore Options - General tab:
-
Clear the Restore to same folder check box.
-
In the Destination Client list, select the computer that hosts the share or mounted file system.
-
In the Specify Destination Path, enter the network share.
Example:
/finite/nftest/test
-
Select the Impersonate User check box.
-
To create the files in the destination folder on the client where you are restoring the data, enter a username and password with permissions.
-
Result
To access the restored data, enter the credentials that you specified in the Restore Options dialog box.
Browse and Restore Deleted Files
-
From the CommCell Browser, expand Client Computers > client > File System > backup set.
-
In the right pane, right-click a subclient, and click Browse and Restore.
-
In the Browse and Restore dialog box, click Time Range or Latest Backup depending on the time when the backup was performed.
-
Click the Advanced Options tab and select the Show Deleted Items check box.
-
Click View Content.
The deleted files are displayed with the backed up files.
-
Select the data that you want to restore, and click Recover All Selected.
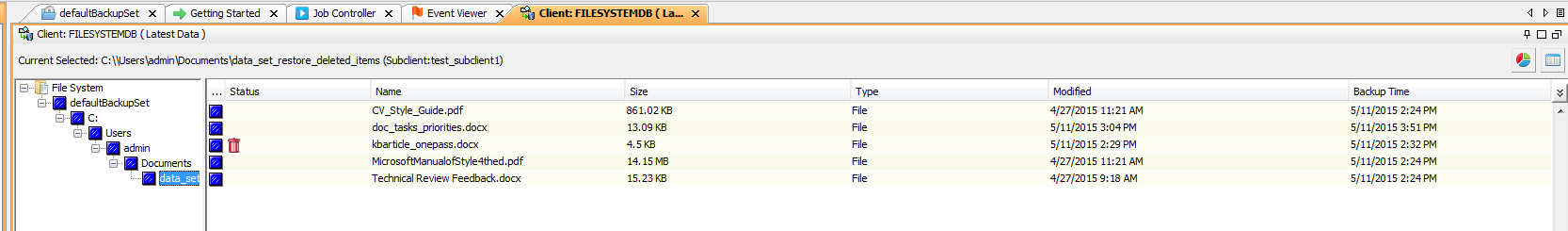
Result
The deleted files are restored to the destination location specified in the Restore Options dialog box.